Embark on a scientific voyage with our in-depth meiosis foldable activity answer key, meticulously crafted to unravel the complexities of cellular division. Delve into the fundamental concepts of meiosis, unravel its intricate stages, and explore its profound applications in various scientific disciplines.
Unveiling the secrets of meiosis, this comprehensive guide empowers students and educators alike to delve deeper into the fascinating world of genetic inheritance.
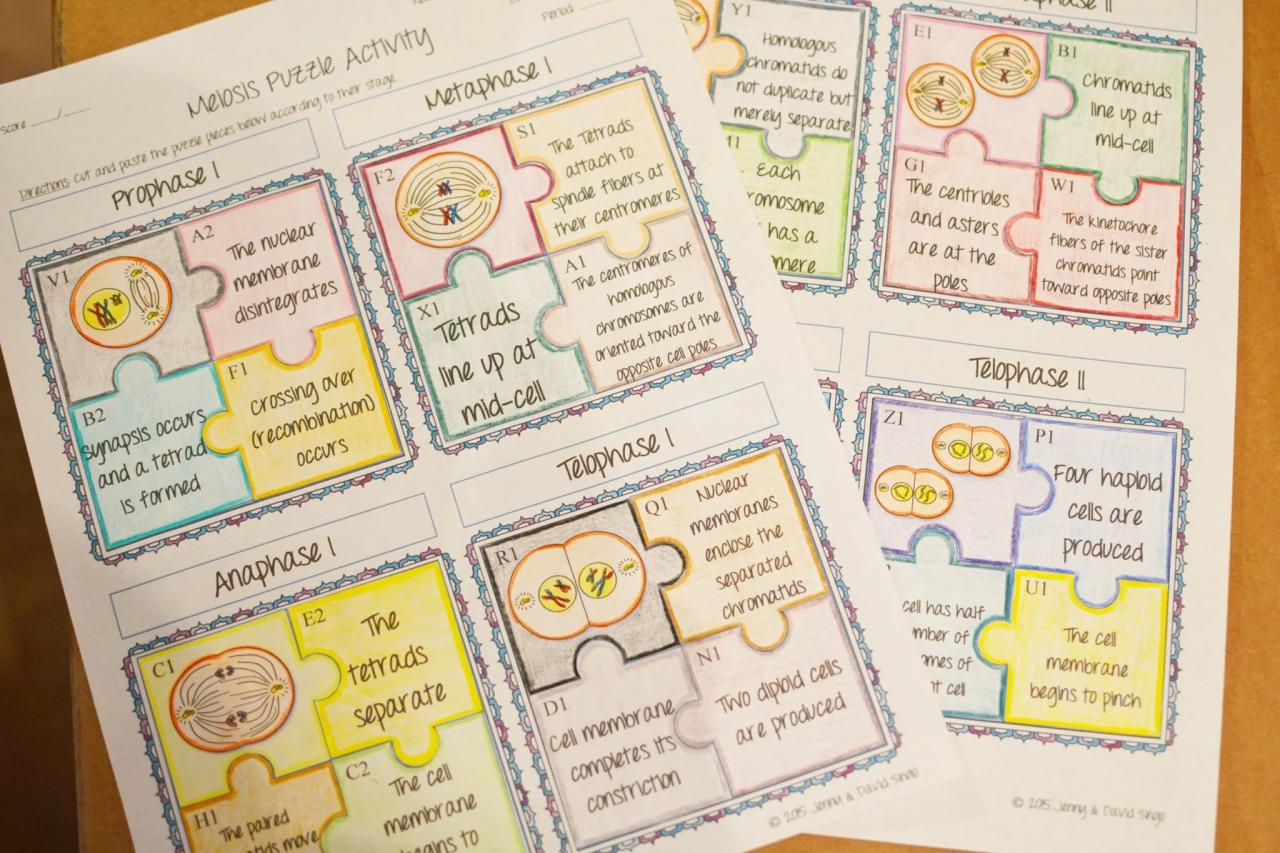
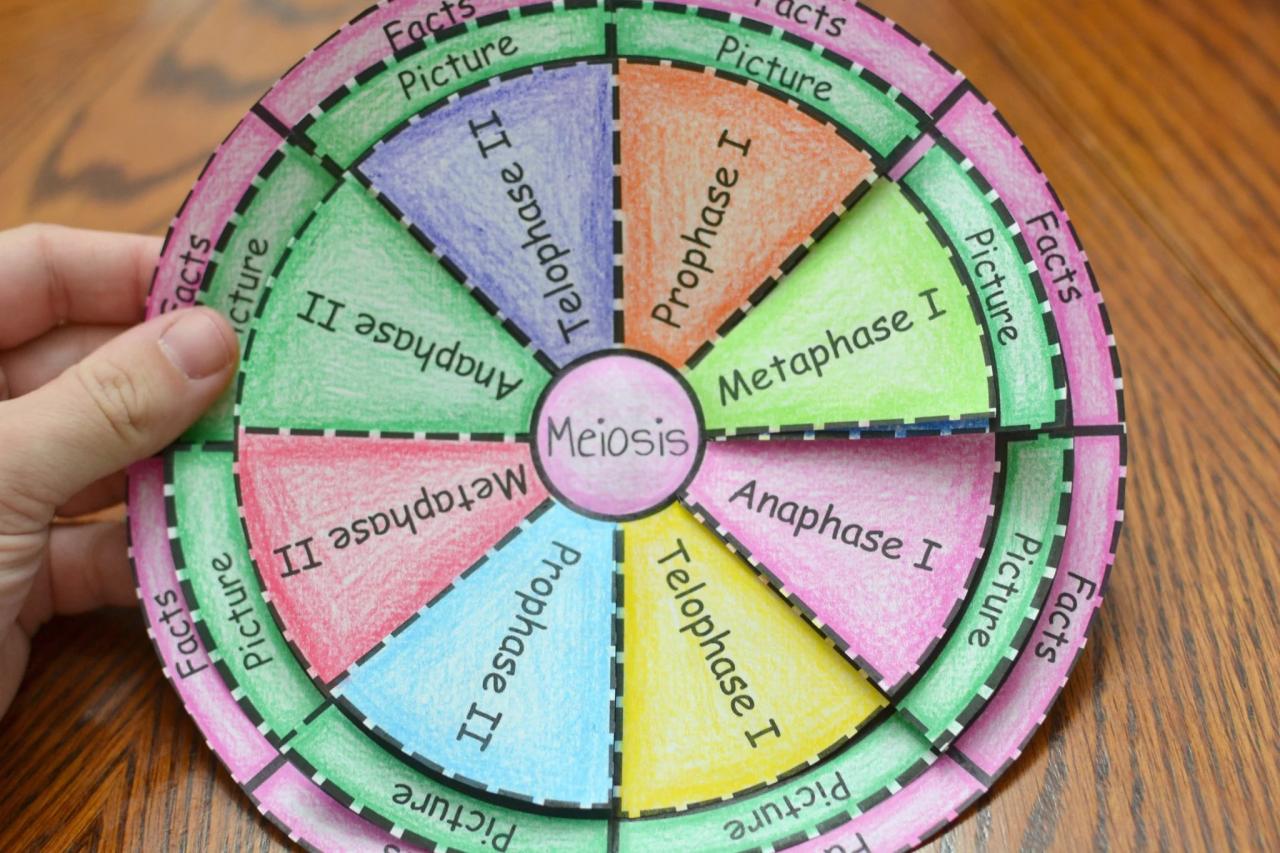
Meiosis Foldable Activity Answer Key
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four haploid cells from a single diploid cell. It is used in sexual reproduction to create gametes, such as eggs and sperm. Meiosis occurs in two stages, meiosis I and meiosis II.
Stages of Meiosis
- Meiosis I:During meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material through a process called crossing over. The chromosomes then line up in the center of the cell and are separated into two daughter cells.
- Meiosis II:During meiosis II, the daughter cells from meiosis I divide again, resulting in four haploid cells.
Examples of Meiosis
Meiosis is used in everyday life in a variety of ways, including:
- Reproduction:Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction. It produces gametes, which are the cells that fuse to form a zygote. The zygote then develops into a new individual.
- Genetic variation:Meiosis shuffles the genes in the chromosomes, resulting in genetic variation. This variation is important for evolution, as it allows for new traits to arise.
- Medical research:Meiosis is used in medical research to study genetic disorders and develop new treatments.
Meiosis Foldable Activity Answer Key
Stages
Stages
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in a cell by half. This process is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that each offspring has the correct number of chromosomes.
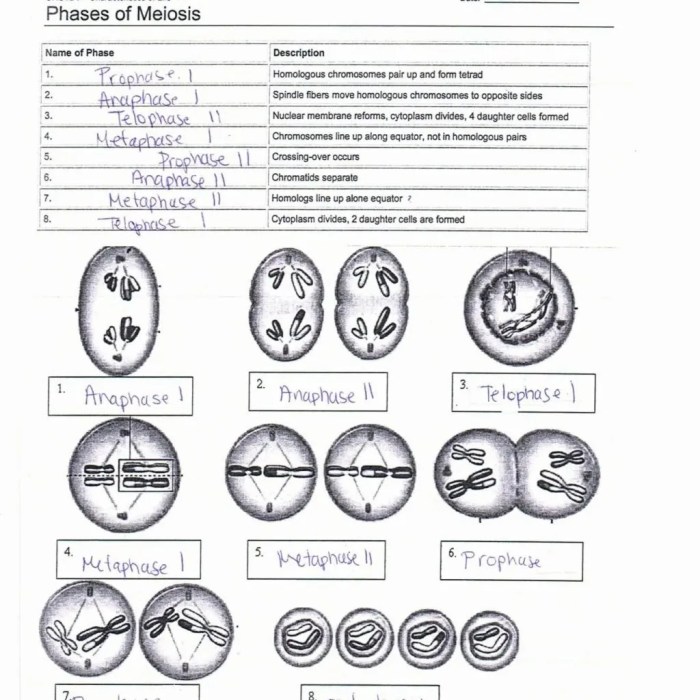
Meiosis consists of two stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Each stage is further divided into four substages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Meiosis I
During meiosis I, the homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material. This process is known as crossing over. The chromosomes then line up in the center of the cell and are separated into two daughter cells.
The purpose of meiosis I is to reduce the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. This is necessary because each offspring receives one set of chromosomes from each parent. If meiosis did not occur, each offspring would have twice the number of chromosomes as its parents.
Meiosis II
During meiosis II, the daughter cells from meiosis I divide again. This time, the sister chromatids of each chromosome separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. The result is four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
The purpose of meiosis II is to separate the sister chromatids of each chromosome. This ensures that each offspring receives a complete set of chromosomes, one from each parent.
Comparison of Meiosis Stages
The following table compares the stages of meiosis:
| Stage | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Prophase I | Homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material. | To reduce the number of chromosomes in the cell by half. |
| Metaphase I | Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. | To ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. |
| Anaphase I | Homologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. | To separate the homologous chromosomes. |
| Telophase I | Two daughter cells are formed, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. | To complete the first stage of meiosis. |
| Prophase II | Sister chromatids of each chromosome separate. | To separate the sister chromatids. |
| Metaphase II | Chromosomes line up in the center of the cell. | To ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. |
| Anaphase II | Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. | To separate the sister chromatids. |
| Telophase II | Four daughter cells are formed, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. | To complete the second stage of meiosis. |
Meiosis Foldable Activity Answer Key
Applications
Applications
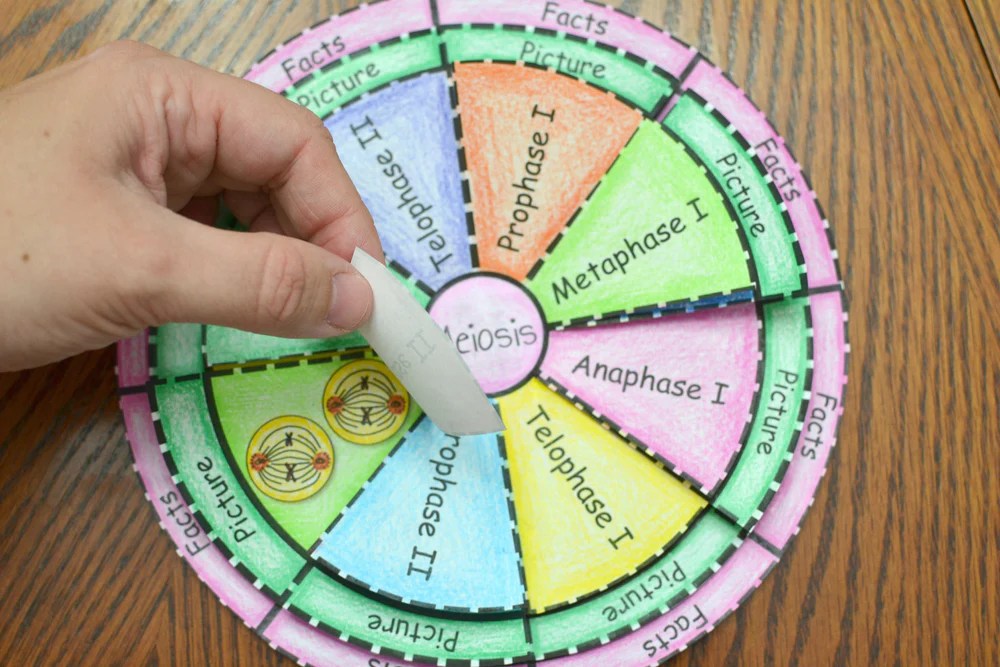

Applications of Meiosis, Meiosis foldable activity answer key
Meiosis has numerous applications in various fields, including genetics, medicine, and agriculture. Understanding the process of meiosis is crucial for comprehending the mechanisms behind genetic inheritance, variation, and the development of new species.
Genetic Engineering
Meiosis plays a vital role in genetic engineering techniques, which involve manipulating the genetic material of organisms. By controlling the process of meiosis, scientists can create organisms with specific genetic traits or modify existing traits. For instance, in agriculture, meiosis is utilized to develop new plant varieties with enhanced resistance to pests, diseases, or environmental stresses.
Medicine
In medicine, meiosis is essential for understanding the genetic basis of inherited diseases and developing treatments for them. Studying meiosis helps researchers identify genetic mutations and variations associated with certain diseases. Additionally, meiosis is crucial for reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), which aim to improve the chances of conceiving healthy offspring.
Meiosis Foldable Activity Answer Key
Resources
Resources

This section provides resources for further exploration of meiosis. These resources include links to websites, books, and videos that offer detailed information on the topic. Additionally, ideas for creating a foldable activity on meiosis are shared to enhance understanding and retention of the subject matter.
Websites
[Khan Academy Meiosis](https
//www.khanacademy.org/science/ap-biology/cell-structure-and-function/meiosis/a/meiosis)
[Biology Corner Meiosis](https
//www.biologycorner.com/anatomy/meiosis.html)
[Amoeba Sisters Meiosis](https
//www.amoebasisters.com/videos/meiosis-the-basics/)
Books
[Essential Cell Biology, 4th Edition](https
//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK9838/)
[Campbell Biology, 12th Edition](https
//www.amazon.com/Campbell-Biology-12th-Lisa-Urry/dp/0134094162)
[Genetics
Analysis and Principles, 8th Edition](https://www.amazon.com/Genetics-Analysis-Principles-Daniel-Hartwell/dp/1605354825)
Videos
[Meiosis
Crash Course Biology #11](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=k5pL-H4SR-8)
[Meiosis Explained Simply](https
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=1-x-d-C_s0w)[Meiosis
An Overview](https
//www.youtube.com/watch?v=I9ywnv2RZ7c)
Foldable Activity Ideas
-
-*Flip Book
Create a flip book with each page representing a different stage of meiosis.
-*Accordion Book
Design an accordion book that unfolds to reveal the key events and concepts of meiosis.
-*Pop-Up Book
Construct a pop-up book with interactive elements that illustrate the processes involved in meiosis.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the significance of meiosis in genetic inheritance?
Meiosis plays a pivotal role in ensuring genetic diversity by creating gametes (eggs and sperm) with unique combinations of chromosomes, facilitating the transmission of genetic material from one generation to the next.
How is meiosis utilized in genetic engineering?
Meiosis is employed in genetic engineering to create genetically modified organisms (GMOs) by introducing specific genes or manipulating existing ones, enabling the development of organisms with desired traits.
What are the key applications of meiosis in medicine?
Meiosis is crucial in reproductive medicine, particularly in assisted reproductive technologies such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), where it ensures the formation of viable gametes for fertilization.