Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells worksheet – Embark on an academic exploration with the Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet, a comprehensive guide that unveils the fundamental differences between these two cell types. This worksheet provides a detailed comparison of their structures, functions, and processes, offering a thorough understanding of the building blocks of life.
Delve into the intricate world of cells, where prokaryotic cells, the simpler and ancient life forms, contrast with eukaryotic cells, the more complex and advanced organisms. Discover the distinct characteristics of each cell type, from their cellular components to their specialized functions.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Cells are the fundamental units of life and can be broadly classified into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells are simpler in structure and lack a nucleus, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and contain a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
The key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are summarized in the table below:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Cell size | Typically 0.1-5.0 µm | Typically 10-100 µm |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
| Cell division | Binary fission | Mitosis |
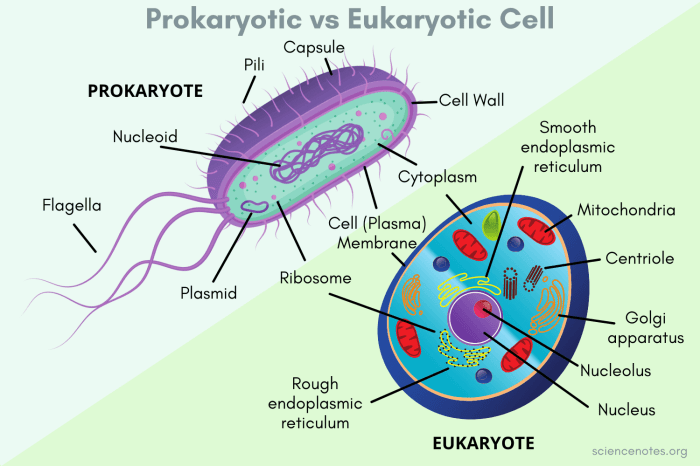
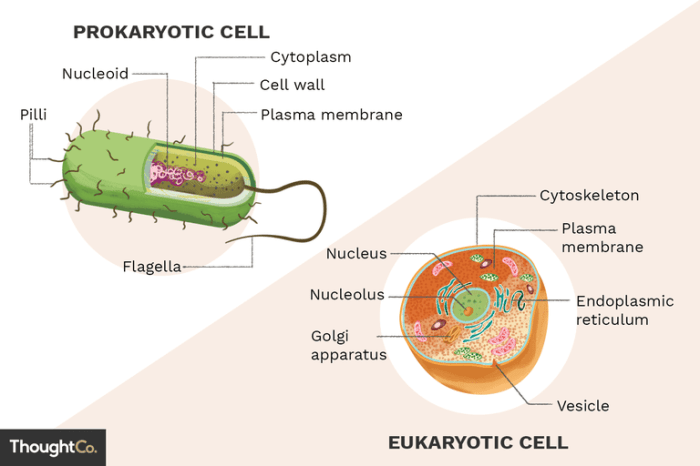
Structure and Function of Prokaryotic Cells

Prokaryotic cells are typically small and lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple structure that includes a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a single circular chromosome.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides protection and support. It is made up of peptidoglycan, a unique polymer found only in prokaryotic cells.
Cell Membrane
The cell membrane is a semipermeable barrier that controls the movement of substances into and out of the cell. It is made up of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the fluid-filled space inside the cell that contains all the cell’s organelles. It is the site of many important cellular processes, such as protein synthesis and DNA replication.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are made up of RNA and protein and are found free in the cytoplasm or attached to the cell membrane.
Structure and Function of Eukaryotic Cells
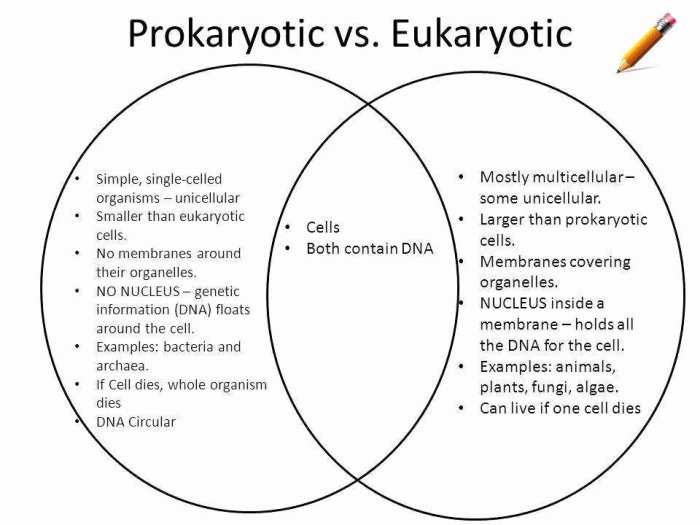
Eukaryotic cells are more complex than prokaryotic cells and have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They are typically larger than prokaryotic cells and have a more organized structure.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material. It is the control center of the cell and is responsible for regulating gene expression and DNA replication.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells worksheet
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that is involved in the modification, sorting, and packaging of proteins.
Mitochondria
Mitochondria are organelles that are responsible for cellular respiration. They are the powerhouses of the cell and produce energy in the form of ATP.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein filaments that provides support and shape to the cell. It is also involved in cell movement and division.
Cell Division
Cell division is the process by which cells reproduce. There are two main types of cell division: binary fission in prokaryotic cells and mitosis in eukaryotic cells.
Binary Fission
Binary fission is a simple form of cell division that occurs in prokaryotic cells. It involves the replication of the cell’s chromosome and the division of the cell into two identical daughter cells.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a more complex form of cell division that occurs in eukaryotic cells. It involves the replication of the cell’s chromosomes and the division of the cell into two identical daughter cells. Mitosis is a continuous process that can be divided into four stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Cell Differentiation and Specialization
Cell differentiation is the process by which cells become specialized in structure and function. It occurs in eukaryotic cells and is essential for the development of multicellular organisms.
Factors that influence cell differentiation include the cell’s genetic makeup, the environment, and cell-cell interactions.
There are many different types of specialized cells in the body, each with its own unique structure and function. Some examples include muscle cells, nerve cells, and skin cells.
Cell Communication
Cell communication is the process by which cells exchange information with each other. It is essential for the coordination of cellular activities and the development and functioning of multicellular organisms.
There are two main types of cell communication: direct and indirect.
Direct Cell Communication
Direct cell communication occurs when cells are in physical contact with each other. It can occur through gap junctions, plasmodesmata, or direct cell-cell signaling.
Indirect Cell Communication
Indirect cell communication occurs when cells release chemical signals that are detected by other cells. These signals can be hormones, neurotransmitters, or cytokines.
Top FAQs: Prokaryotic Cells And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
What are the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess a nucleus and a variety of membrane-bound organelles.
What is the function of the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
The cell wall provides structural support and protection for the prokaryotic cell.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis, lipid synthesis, and detoxification.
