Exercise 6 review sheet classification of tissues – Embark on a journey into the realm of tissue classification with Exercise 6 Review Sheet. This in-depth guide unveils the intricacies of different tissue types, providing a solid foundation for understanding their significance in the human body.
Delve into the diverse characteristics, functions, and examples of epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissues. Prepare to expand your knowledge and gain a comprehensive understanding of the building blocks of life.
Classification of Tissues
Tissue classification is the process of categorizing tissues based on their structure and function. It is important to understand tissue types because they provide the foundation for the structure and function of organs and organ systems. Tissues are classified into four main types: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
Epithelial Tissue: Exercise 6 Review Sheet Classification Of Tissues
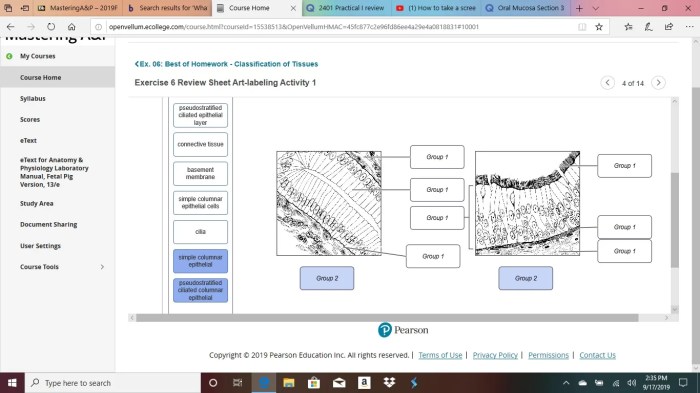
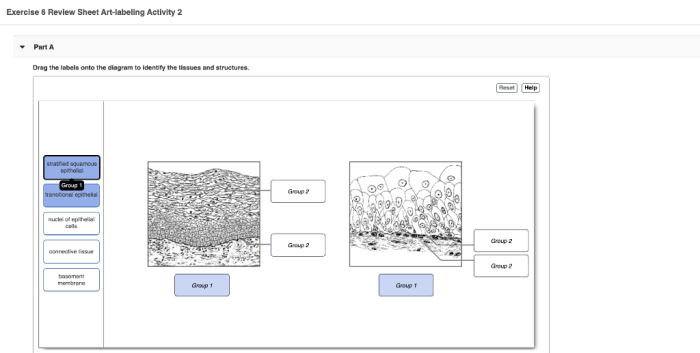
Epithelial tissue is a type of tissue that covers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body. It is composed of cells that are closely packed together and have little extracellular matrix. Epithelial tissue has a variety of functions, including protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion.
Characteristics of Epithelial Tissue, Exercise 6 review sheet classification of tissues
- Cells are closely packed together
- Little extracellular matrix
- Covers the surfaces of the body and lines the cavities of the body
Functions of Epithelial Tissue
- Protection
- Secretion
- Absorption
- Excretion
Examples of Epithelial Tissue
- Skin
- Lining of the digestive tract
- Lining of the respiratory tract
- Lining of the urinary tract
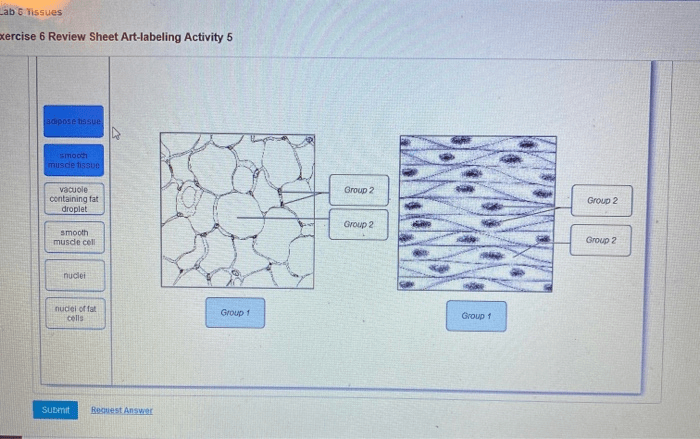
Connective Tissue
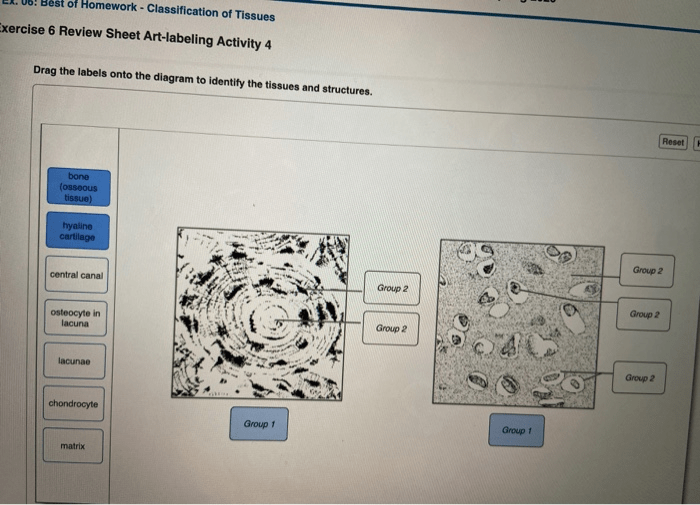
Connective tissue is a type of tissue that connects and supports other tissues in the body. It is composed of cells that are embedded in a matrix of extracellular material. Connective tissue has a variety of functions, including support, protection, and transport.
Characteristics of Connective Tissue
- Cells are embedded in a matrix of extracellular material
- Connects and supports other tissues in the body
Functions of Connective Tissue
- Support
- Protection
- Transport
Examples of Connective Tissue
- Bone
- Cartilage
- Ligaments
- Tendons
Muscle Tissue
Muscle tissue is a type of tissue that is responsible for movement. It is composed of cells that are specialized for contraction. Muscle tissue has a variety of functions, including movement, posture, and heat production.
Characteristics of Muscle Tissue
- Cells are specialized for contraction
- Responsible for movement
Functions of Muscle Tissue
- Movement
- Posture
- Heat production
Examples of Muscle Tissue
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle
Nervous Tissue
Nervous tissue is a type of tissue that is responsible for communication and control in the body. It is composed of cells that are specialized for the transmission of electrical signals. Nervous tissue has a variety of functions, including communication, control, and coordination.
Characteristics of Nervous Tissue
- Cells are specialized for the transmission of electrical signals
- Responsible for communication and control in the body
Functions of Nervous Tissue
- Communication
- Control
- Coordination
Examples of Nervous Tissue
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Nerves
FAQ
What is the primary function of epithelial tissue?
Protection and secretion
Name the three types of muscle tissue.
Skeletal, smooth, and cardiac
How does connective tissue support the body?
By providing structural support, cushioning, and protection
